We previously discussed how in today's fast-paced business environment, the need to deploy employees to work outside of their home country can sometimes lead to many short-term assignees travelling on a business visa to avoid the expense and bureaucratic process of getting work authorisation. In addition, many managers may inadvertently create ‘stealth’ expats by asking short-term assignees to stay on for another month or two, thereby creating host country tax and social security withholding requirements, and possibly immigration infringements too. ECA has also observed more ‘floating employees’ sent to work in countries where the employer has no registered entity and this potentially could create a corporate tax presence for the non-resident employer. To account for these risks and to keep pace with an internationally mobile workforce, companies need to rethink how they structure employment arrangements, policies and processes accordingly.
Important issues to consider include:
Contractual arrangements
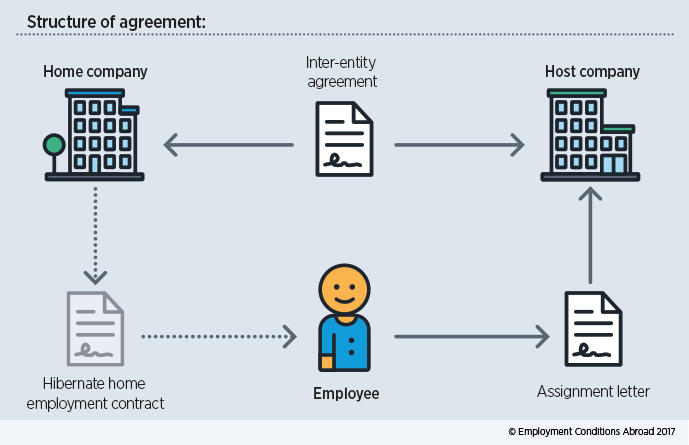
When an employee is sent on a short-term assignment, the individual is typically issued with an 'assignment letter', or 'assignment agreement'. This letter outlines the benefits (allowances, reimbursements, etc) that the employee is entitled to receive during the period of assignment to the host entity. However, it is important to consider how any underlying employment contract, with the home company, interplays with the separate assignment letter. In general, an employee on a short-term assignment remains an employee of their home company during the length of the assignment, but with certain rights and benefits suspended/hibernated and replaced by relevant terms and conditions contained within an assignment letter. Hibernating a home country contract can, however, complicate potential dismissals as the home country contract has not been terminated, but will ‘spring back to life’ at the natural end of an assignment or once an assignment has been terminated.
The role of an assignment letter (agreement)
Short-term assignments are highly complex. Hence, it is crucial to have proper documentation in place to clarify and provide guidance. An effective assignment letter not only benefits the employee, but also the employer (HR, legal, tax and payroll, for instance). The assignment letter should clearly spell out the compensation and benefits (per diems, reimbursements, serviced accommodation costs etc) that the employee would receive during the short-term assignment, thus making all parties aware of assignment entitlements and mitigating any dispute or retroactive negotiations in the future.
An appropriately drafted assignment letter can also minimise potential financial or reputational risk for non-compliance and help mitigate potentially adverse corporate tax implications. So, it is important that the assignment letter documents the responsibilities of the home and host country companies if the economic employer principles discussed below are to be avoided. Hence, it should address such issues as:
- The assignment start and intended end date;
- The employee’s specific duties while on assignment;
- The employing entity while on assignment;
- To whom does the employee report while on assignment?
- Who determines the holidays and work hours of the employee?
- Who will be responsible for any disciplinary issues during the assignment?
- Who can terminate the contractual arrangements entered into with the employee?
How long an assignment is anticipated to last has an important bearing on immigration and tax compliance regulations. For example, in the United States, it is possible to exclude certain travel, meals and accommodation expenses from federal tax if an assignment is expected to last less than 12 months. However, should the assignment length change from less than one year to greater than one year, the expenses previously considered non-taxable would be deemed taxable from the date of the change in ‘intent’. Consequently, the anticipated or intended assignment duration should be supported through appropriate language in the assignment letter.
The choice of language used in an assignment letter can also have implications for the taxability of certain allowances and benefits. For example, there is a distinction between an employee sent to Japan for business travel and one sent under a secondment arrangement. An employee ‘seconded’ on a short-term assignment to Japan cannot exempt income from taxation under the 183-day rule, whereas a ‘business traveller’ or ‘visitor’ can potentially do so based on facts and circumstances. An assignment/secondment agreement for employees sent to Japan for short-term projects should therefore use consistent terminology to qualify for the preferential tax treatment.
Cost allocation
Who picks up the costs of a short-term assignment can be a source of much debate in many organisations when an employee is temporarily assigned to work in another country. This is because costs need to be borne in the correct location to ensure that the appropriate tax deductions can be claimed by the group.
Consider the potential tax risks when an employee is being assigned internationally to another company within a group. Certain tax authorities adopt an ‘economic employer’ approach to interpreting Article 15 of the OECD model treaty which deals with the Dependent Services Article (economic employer is discussed further here). One of the conditions of Article 15 states that if the assignee’s salary and costs are recharged to the host entity, then the host country tax authority will treat the host entity as being the ‘economic employer’ and therefore the employer for the purposes of interpreting Article 15. In this case, tax relief would be denied and the employee would be subject to tax in the host country even if the individual spends less than 183 days there. Short-term assignments can also create a corporate tax liability in the host jurisdiction if cost allocation is not carefully managed.
To help minimise any unexpected tax surprises, it is advisable to put an agreement in place, which specifies how costs will be managed during an assignment. An inter-entity agreement should be drawn up between the host company and the assignee’s home company. This agreement governs how costs associated with the assignment will be funded. An inter-entity agreement is in addition to the assignment letter (agreement) between the employee and the home company.
 Policy
Policy
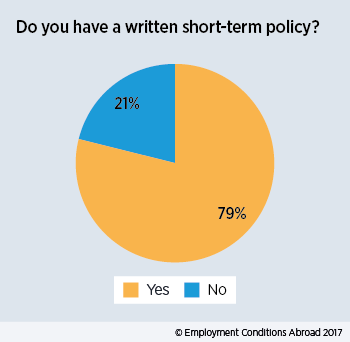
Short-term assignments now take all shapes and forms, with short-term projects, weekly commuters, and extended business trips becoming more common. A written short-term policy can be a cost-effective tool as it provides discipline and a framework that enables equity of treatment amongst assignees and reduces the number of employees negotiating their own packages. It can set out logically the steps to be taken in any relocation and the procedures to be followed.
It is advisable that each category of short-term assignment be housed in a separate policy document, as there is a possibility that employees will attempt to leverage off the best parts of other packages to suit their particular circumstances. Additionally, a short-term policy should be regularly evaluated against the current industry trends as well as the company’s business goals to make sure it is fit for purpose.
The short-term policy should address the following key issues:
- Should any host country tax liability arise, will the assignee receive any tax assistance?
- Will the assignee be on the host country payroll, home country payroll, an international assignee payroll, or multiple payrolls?
- Will the assignee’s pay be protected from exchange rate volatility?
- What happens when short-term assignments are extended and change from one assignment category to another?
Managing exceptions
Exceptions to policy can be difficult to manage, requiring negotiations between the mobility team, the assignee and the business line for approval. They can also be costly, triggering unaccounted-for expenses and untracked ‘budget creep’, the impact of which is rarely calculated or consolidated across the business functions.
Exceptions should only be granted under very limited circumstances and require written explanations and approval of the executive board or HR director. If carefully monitored, the number of exception requests can indicate that a particular process or policy component requires re-design or further instruction to a vendor.
To ensure global equity and minimise budget creep, consider:
- Creating a detailed policy governance process for identifying and capturing deviations to policy or process with a view to reducing or eliminating exceptions;
- Setting up a centralised system to manage and approve exceptions to help minimise expenses;
- Establishing a process owner for short-term assignments, someone with responsibility and authority to monitor and report on trends in exceptions;
- Creating a formal short-term assignment policy, as mentioned above, to minimise exceptions and foster consistency and clear communications.
Tracking potential risks
Tax and immigration irregularities are common for employees on short-term assignments. Accordingly, it is important to develop an education programme for employees and their managers to inform them about the risks of cross-border work and the consequences of non-compliance.
Work permit and immigration infringements should not be underestimated as the penalties for individuals working outside their home country without the appropriate work authorisation can be harsh. Not all short-term assignees need immigration approval, but then again, some do. It is important to note that just because an employee may not trigger any host country tax liability it doesn’t follow that they are exempt from immigration requirements. Indeed, staying on the home payroll is one of the most common areas of risk for short-term assignees and it is not an indication that immigration approval is not required.
For many companies, technology has become the key to achieving and maintaining compliance. Without proper monitoring, an employer may unwittingly be exposed to tax and social security risks. Diligent tracking of short-term assignees and a solid process to be able to identify risks up-front are key to ensuring compliance.
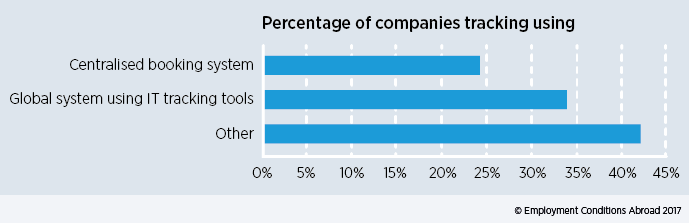
Source: ECA’s Managing Variety in International Mobility survey
Once a company’s short-term population reaches a certain size, manual tracking of policy exceptions using Excel spreadsheets is unlikely to be sufficient to ensure compliance with now greater information sharing among tax and immigration authorities. So, if companies want to be ahead of the curve in managing short-term assignees, they need to start tracking them. This will require communications to be established between the business units, tax, HR, legal, payroll, etc early in the assignment planning process, as well as when any assignment extension is contemplated.
Coordination with payroll
At the heart of the administration process is the payroll team and it is essential that the appropriate home and host country payroll personnel are involved in planning for short-term assignments. They are ultimately responsible for ensuring the accurate and timely delivery of the assignment package to employees, while managing the local jurisdiction compliance requirements with regard to tax and social security withholding.
The home country payroll must be informed of the intended assignment duration and assignment package to be paid to the employee. The home payroll will need to understand whether the allowances and benefits will or will not be considered taxable to the employee.
Assignment income, such as a short-term allowance or per diems, is often paid through the home country payroll to comply with standard tax treaty rules. Typically, if income is to be exempt of host taxes, the payroll costs should not be borne by a permanent establishment in the host country.
If an employee triggers a tax liability, many host countries will require withholding of income taxes through a local payroll. Consequently, the host country payroll will need to be informed of the assignment package the employee is receiving to understand if these may be considered taxable in the host country, even if they are not taxable in the home country. The host payroll will also need the relevant social security applications to be made to ensure that contributions are paid to the appropriate tax authorities.
Finally
Our three-part series of articles on short-term assignments has highlighted some of the complexities in structuring short-term assignments, and some of the challenges concerning immigration, payroll reporting and tax compliance. With proper planning and administration, short-term assignments can be an effective and efficient means of increasing the pool of potential employees for the international assignment programme.
FIND OUT MORE
Please contact us to speak to a member of our team directly.